U3+U4
ARQUITECTURE THROUGHOUT HISTORY
THE ORIGINS
Australopitecus first appeared in central africa, and had no need for shelter.
1.600.000-200.000 B.C.
Homo erectus develops the concept of home, built around a fireplace. Huts were developed
Australopitecus first appeared in central africa, and had no need for shelter.
1.600.000-200.000 B.C.
Homo erectus develops the concept of home, built around a fireplace. Huts were developed

100.000-40.000 B.C.
Homo Neanderthalensis inhabits caves, and acknowledges the movement of the sun

40.000 B.C.
Homo sapiens develop circular huts, waterproofed by the use of a layer of pelts
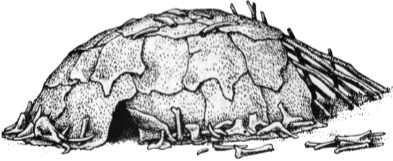
8.000 B.C.
Groups of rectangular houses are developed, and the first city is born in 5.500 B.C. Agriculture is firmly established, and sedentary life is encouraged. The city enclosure was protected by a defensive wall

4.000 B.C.
PROTOHISTORY. Cities are built in the along the nile, in its proximities, in order to be able to farm in humid, fertile terrains. Religious buildings are developed, and contructed at high altitude, in order to worship the gods closer to them. (ziggurats)

3.500 B.C.
EGYPTIANS. The egyptians felt life was too good to end, and developed monuments that reflected the cult of the dead. The egyptian civilization lasts almost 3,000 years, and in that time, temples and pyramids were constructed in accordance to this cult.

1.200 B.C.
GREEKS. Houses had a central courtyard and public places are designed. (Theaters, Stadiums, the Agora) Greek architecture is characterised for searching for equilibrium between vertical and horizontal load bearing elements. (colums and beams)
Iktinos and Kallikrates were the architects credited with designing the Parthenon


1.100 B.C.
ROMANS. Discovery of concrete, and develpoment of Basilicas, aqueducts, roads, sewage networks, arches and domes. With the discovery of concrete, roman architects were able to experiment with interior space, and natural light and shadow.
Marcus Vitruvius Pollio was the architect of Julius Caesar from 58 to 51 BCE. Not only did he build several structures, but he also traveled extensively around the Mediterranean to study architecture

476 A.D.
The western roman empire disappears. What was left of the empire was christianized, Pictorial sculptural and constructive techniques wew lost, as well as everything that was not justifiable by christianity.
6th Cent.
BYZANTINE Architechture is preminently religious
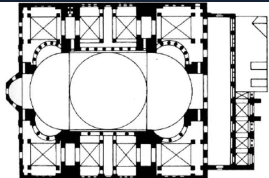
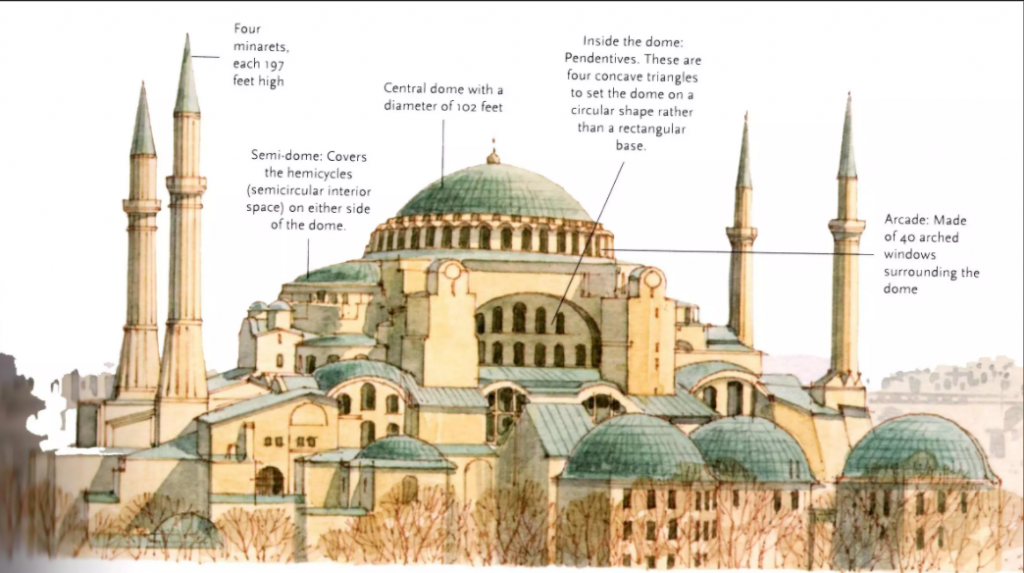
6th – 8th Cent.
LOMBARDS occupy roman buildings and develop decorative elements

7th – 8th Cent.
VISIGOTHS develop eclessiastical arquitecture, based on the traditional roman basilica, influenced by sirian forms.

9th Cent.
CAROLINGIAN For the first time since the fall of the roman empire, palaces, cathedrals and monasteries are built.
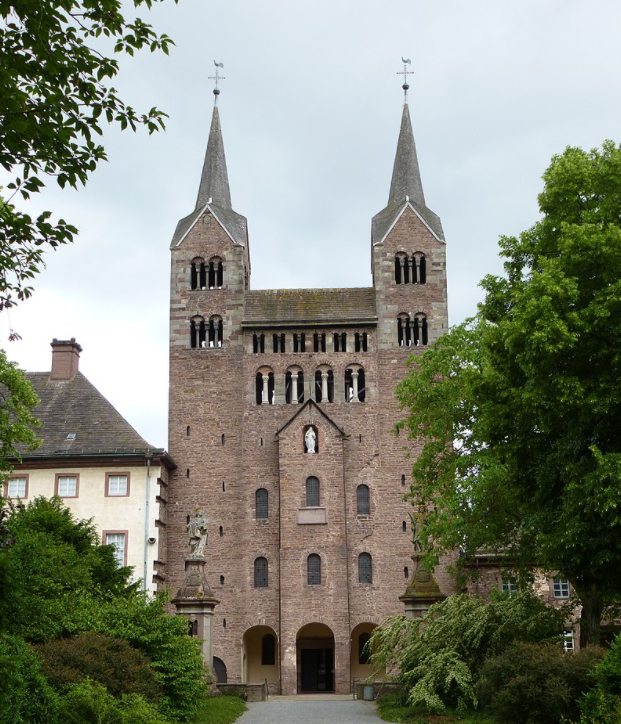

9th – 10th Cent.
SAXONS– Their innovations include galleries,

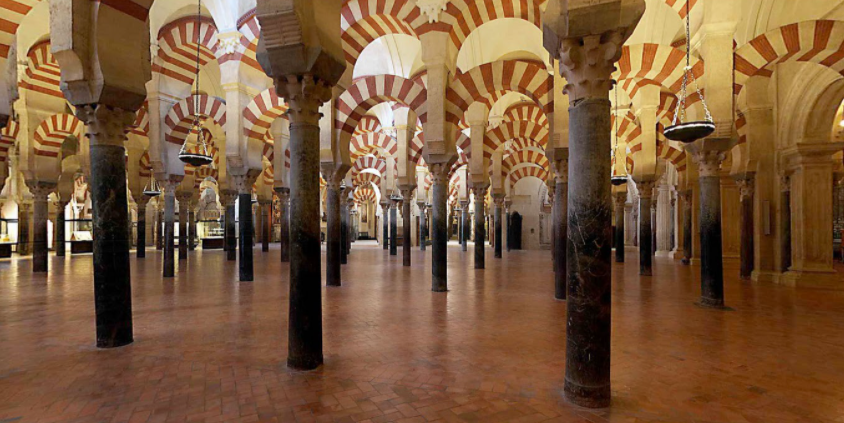
8th – 15th Cent.
ISLAMIC arquitecture produces new religious building typologies such as mosques


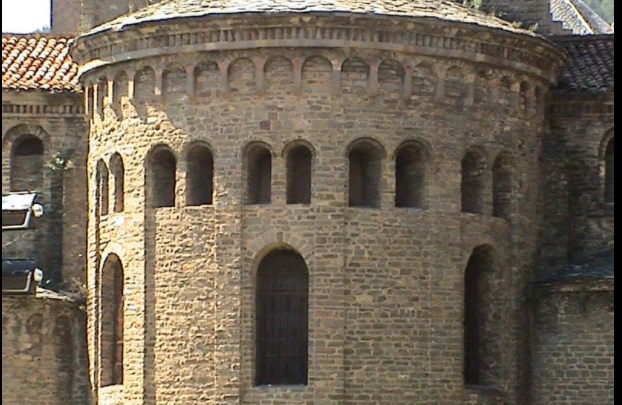
10th – 12th Cent.
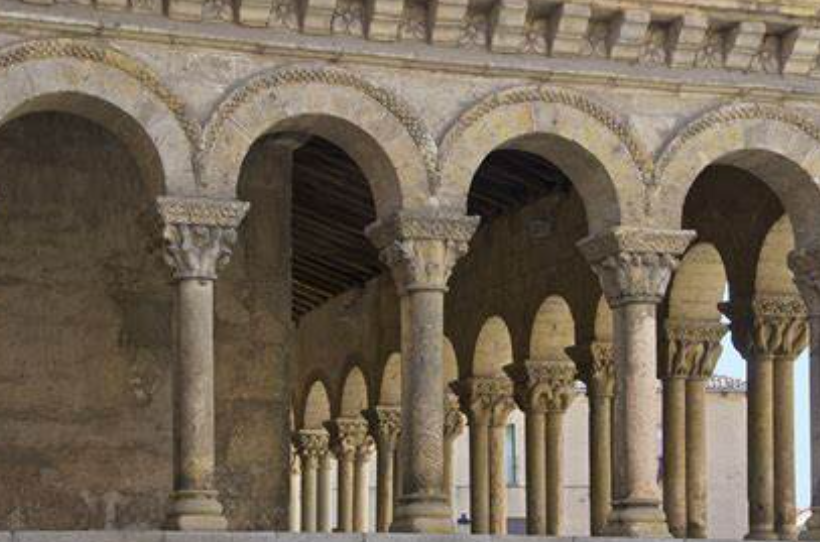
ROMANESQUE Spread through Europe due to pilgrimage, and was characterised by the use of arches


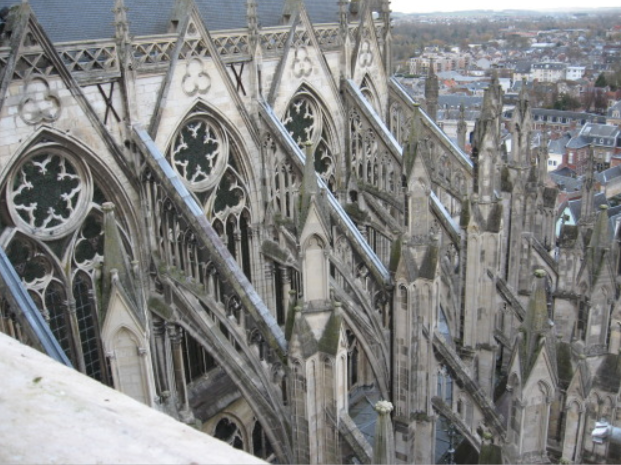
12th – 16th Cent.
GOTHIC The great innovation of this style was the OGIVAL ARCH

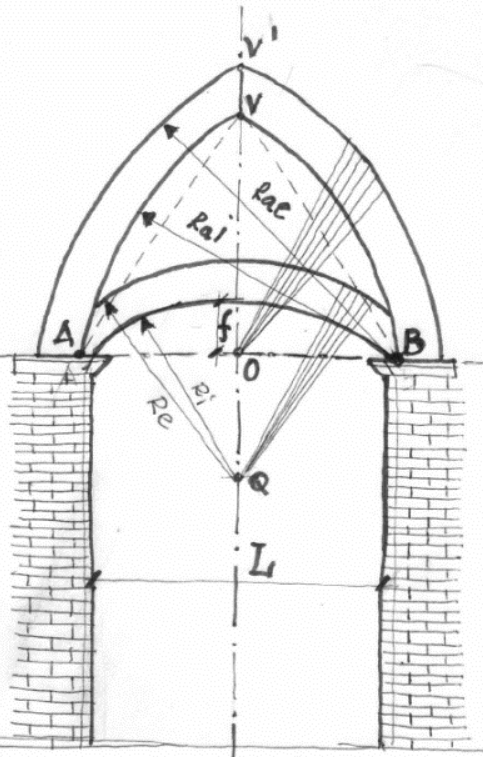
15th-16th Cent. REINASANCE
Humanism emerges, which emphasizes the achievements oh human, distinguishing them from religion. There is an interest to recover Romanism, and Vitruvius´s books are reproduced and studied. Perspective is rediscovered.
FILLIPO BRUNELLESCHI formulates the bases of mathematical perspective, and applies them to architecture

LEON BATTISTA ALBERTI one of the gratest in both theory and practice, known for facade remodels

ANDREA PALLADIO
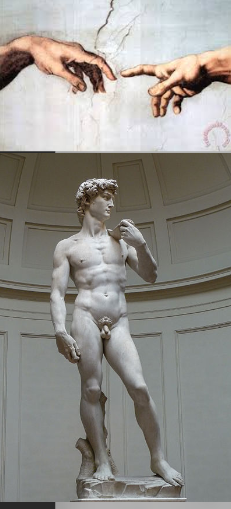
MICHELANGELO BUONARROTI one of the greatest sculptures, painers and architects

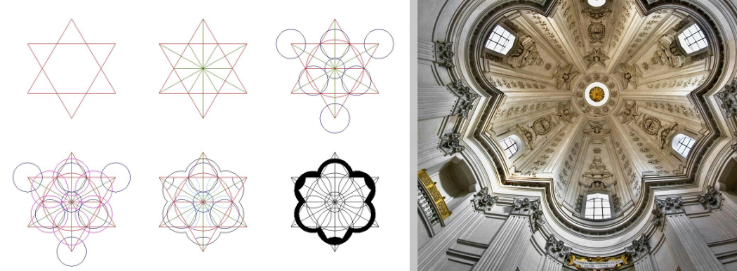
17th – 18th Cent. BAROQUE
Emerged as propaganda and glorification of aristocratic power (Monarchy and eclesiastical power) The dividing line between reality and illusion becomes blurred, with decorations and paintings on ceilings and walls that rise toward the sky, framing, mainly eclesiastical scenes.
GIAN LORENZO BERNINI

FRANCESCO BORROMINI Based on simple geometric elements
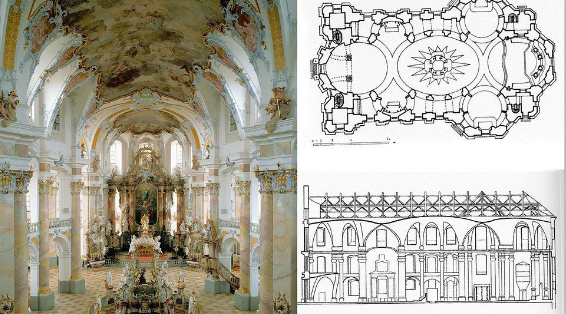
ROCOCO More of an artistic fashion, than an architectural current, born in courtly french buildings. The cluster of elements aims for suprising ostentation. Movements like rococo will raise the unease of other social classes ultimately leading to the French Revolution.
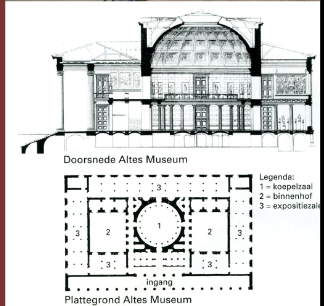
18th – 19th Cent. NEOCLASSIC
Age of enlightment. The neoclassical style was linked to the idea of public service and education.

19TH CENTURY
The architecture of industrialization is related to new construction typologies. An industrial spirit is reflected. In response to this frigid spirit, historicism arises, as a way to evade reality and to fulfill the desire to cling to the past. Historicism includes movements such as neo-Gothic, neo-Egyptian, neo-Romanesque…..


20TH CENTURY
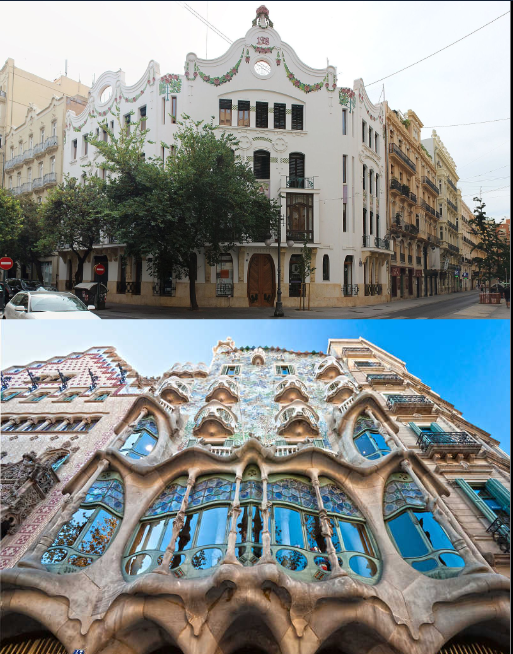
ART-NOUVEAU includes modernism, liberty, jugendstyl. Modernism developed in Catalonia at the end of the 19th Century

HISTORICAL AVANT GARDE (1900-1914) cubism, expressionism futurism

AVANT GARDE BETWEEN WARS (1913-1932) surrealism, abstractism

POST WAR PERIOD (1950-present day) THE TIME OF REVOLUTIONS, UTOPIAS, PROPOSALS WITH MUCH PRACTICAL AND THEORICAL EXPERIMENTATION

BIBLIOGRAPHY